Process safety management under OSHA
In 1912 the first Industrial Revolution took place and a lot of accidents happened and gases emancipating from Chimneys and faulty machines were installed. Lots of people died and were not noticed. Then World War 1 came in 1914 and ended in 1919.
Because of that nothing could be done to prevent accidents and deaths immediately. Then the second industrial revolution came in 1925, then the same story of people dying due to hot gases and faulty machines.
*What is safety:
Safety is a relative freedom from diseases, fire and floods or by any other means or accidents.
Example: When you walk on the road pavement, suppose you trip and fall on the pavement it is personal safety.
*Risk:
Risk means the likelihood of specific effect with a specific period
due to complex of probability
Consequence of vulnerability.
Example: Suppose a man going in a highway in a car, a man criss- crosses, in order to avoid him if you share your wheel to the right or left from the wrath, otherwise get injured in the process.
Risk and safety for your brothers and sisters. You have safety in force and you can avoid risk.
*Hazard means which can be of anything or change whether it is a physical hazard or chemical hazard.
Example: Lots of gases emancipating from the Chimneys and they should be controlled in such a way people should not be affected.
*Environment means free pollution from air.
Example: Delhi is a polluted city in India and prevention is be taken to prevent water pollution:
History of OSHA:
In 1912 the first Industrial Revolution took place and a lot of accidents happened and gases emancipating from Chimneys and faulty machines were installed. Lots of people died and were not noticed. Then World War 1 came in 1914 and ended in 1919. Because of that nothing could be done to prevent accidents and deaths immediately. Then the second industrial revolution came in 1925, then the same story of people dying due to hot gases and faulty machines. People suffered enormously due to carelessness of the factory owners and the government in Europe and in Britain. Then the Second World War came into being in 1939 and ended in 1945. Recording to see safety people were educated and wanted to do something costly to ward off injury and due to accidents.
The Air act amendment came into being in the year 1970 to avoid pollution and other steps were taken.
Then the Bhopal incident in India caused 2000 deaths and the Texas blast killed 123 people the Three Mile Island disaster.
How did the Bhopal accident occur?
Background
The union carbide was built in 1969 to produce the pesticide Sevin using the brand name carbaryl using methyl isocyanide as an intermediate.
The Local Trade union complained of pollution within the plant. A worker accidentally was splashed with phosgene gas as he was carrying out a maintenance job of the plant pipes. In panic he removed the mask and inhaled phosgene gas leading to death in 72 hours.
Journalists reporting in the newspaper columns or sitting on a volcano.
In January 1982 due to phosgene gas leak all the workers number 24 were admitted to the hospital. None of the workers were ordered to wear masks to wear protection equipment. Month Later a chemical engineer came into contact with liquid MIC resulting in 30% of the burns and he died later.
Liquid MIC storage tanks:
Bhopal union carbide India Limited housed three underground 68000 litres of 18000 gallons of MIC in three tanks namely E 610,E 611 and E 619. Safety regulations should be not filled with more than 50% that is 30 tons liquid MIC. E610 contained 42 tons of liquid MIC. Flare Tower was out of action. An attempt was made and could not be done.
Gas leak:
By early December 1984 most of the plant's safety systems were Malfunctioning. Several vent pipes and boilers were intended to clear the pipes. During the late December 2nd evening water believed to have entered through a side pipe water entered subsequently resulting in a runaway exothermic reaction which has accelerated high ambient temperatures variation of other factors, the presence of iron corroding the pipes. The pressure was 2 psi at 10.30 pm. It reached 10 PSI by 11:00 p.m.
Two different senior refinery employees said the mall function of the instrument. By 11:30 pm workers in the MIC area were feeling the effects of MIC and began to look for a leak. It was reported after the tea time that it will be looked after.
In 5 minutes after the tea break, the reaction in the tank E 610 reached critical state at an alarming rate and went up to 40 PSI. One employee noticed a concrete slab on the top of the tank cracked as the energy relief wall just opened. Pressure continued to increase 55 PSI. Direct atmospheric venting has been prevented at least partially by 3-safety devices off Mall functioning and operable.
- A refrigeration system to cool the tank temperature of the gas has been removed. High along temperature
- A flare tower to burn the gas in the connecting pipe was removed.
- scrubber which had been deactivated. About 30 tons of MIC escaped into the atmosphere in 45 to 60 minutes and then increased to 40 tons.
Two Wailing sirens have been deactivated since 1982. Bhopal police was informed of the leak early by the employee and they informed the Hamida hospital first as ammonia and then the union carbide India Limited informed the police. From 2 to 4:30 am. Nobody knows since MIC gas has a tendency to fall towards the ground.
Thousands of people the following morning. 30,000 people were injured. Lot of commotion was among the people. Union says it is the fault of the management's failure and the management says the worker has done the job. William Alexander, union carbide chairman was allowed to fly out there on the 6th December.
Lot of legal action went around. At last 450 million dollars was given by the management as an out of court settlement. Money has not reached the affected people. The issue is still pending in the International Court of law at the Hague. Still people are suffering even after 30 years of the Bhopal blast.
Phillips petroleum Company disaster
Phillips petroleum company disaster near Houston in Pasadena, Texas. The blast occurred 3.5 Richter scale and configuration took 10 hours to bring under control.
The result occurred from your release of extremely(68000 lac ) tons of high-density Poly- ethylene plastic material to make milk containers and other pet bottles. Total employees were around 1500.
The accident occurred and reported the release of flammable gases of 85000 Pound were to release instantaneously through an open valve.
During maintenance isolation valves are closed and compressed air hoses that attach them physically disconnected as a safety measure. The air connection opening and closing the valves were identical and had been improperly reversed when lost Re connected. As a result the world would have been open to why the switch was in a closed position. When the world was opened it had to stay closed. And finally the reactor is up to air. Vapor cloud form came in contact with ignition and exploded 2.4 TNT . The next polyester polyurethane reactor came into contact because of the domino effect. Explosion took place at 1:00 p.m. On 23rd October 1989. 23 people killed and 313 people injured. 6 reactors were destroyed in the near vicinity. The fire was brought out in 10 hours.
The findings of OSHA
- lack of process hazard analysis
- inadequate standard operating procedures
- Non fail safe block valve
- In adequate lock/ tag procedures
- inadequate ventilation
- crowded process equipment.
Three Mile Island disaster;
The accident was a partial meltdown of Three Mile Island nuclear generating station in 1979.
The accident linked failures in the non-nuclear secondary system and Pilot operated relief valve in the primary system. In resulting large coolant to escape.The Mechanical failures compounded by the initial failure of plant operators resigned to the situation as a loss of coolant and accident due to inadequate training and human factors.
In this particular incident , the hidden indicator light operator manually avoided the automatic emergency cooling system of the reactor. Operators believe there was too much cooling and water in the present causing the steam pressure to get inside.
Background:
In the night time hours before the incident, the TM-1 reactor was running at 97% power. Then the team TI M one reactor shutdown for refueling. Main chain of events leading to the partial core meltdown started at 4 a.m. Began in the PM 12 secondary loop. One of the water/ steam loops in a pressurized water cooler.
Initial case of the accident happened during an attempt by reactors overheating and malfunction of the valve calling the water pump tripped. No indication of water pumps in the panel was showing this caused the major active radiation that happened because of the reaction.
Emergency declaration and immediate aftermath:
At 7 hours in the morning an emergency was declared and a general emergency of the plant was done.
Mitigation policies:
Voluntary evacuation: Schools were closed to residents to stay indoors formers to not keep their animals inside.
Lessons learnt:
Multiple failures occurred because of the complex system of the reactor.
Total shutdown of the plant happened in September 2019.
All these major disasters chemicals draw national attention for Major catastrophes. Hazard chemical releases continue to pose a significant threat to employees and to provide impetus internationally and nationally.
In 1990 OSHA proposed the management of hazard associated with hazardous chemicals and established a comprehensive management program that integrated Technologies procedures and management practices.
Notice proposed a standard for the process safety management system of highly hazardous chemicals and commenced the scheduled hearing in Washington DC. That in Houston Texas additional issues until. 1991.
Then the hearings on the proposal were held in Washington DC from November 1990 till March 1991. Old received more than 175 more comment phones to the rule making 4000 pages of testimony and 60 post hearing comments. The final text of the final OSHA document registered in February 1992. Under the Air clean act amendment was enacted as a law in 1990,OSHA was standardized
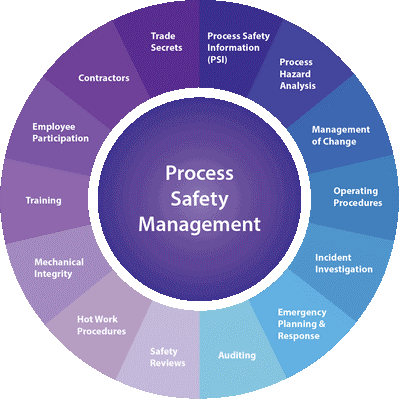
In coordination with the U.S Labor safety department. At last they made it compulsory for all industries in the US and in Europe and Britain and in Gulf countries. In the process safety management system under which 14 elements initially and then as 17 elements now.
The problem:
The unexpected release of toxic , reactive or flammable liquids and gases in processes involving highly hazardous Chemicals have been reported for many years. Incidents continue to occur in various industries that are highly ordered chemicals which may be toxic reactive flammable or explosion or may exhibit a combination of the properties.
Develop safety information identifying workplace chemicals and processes hazards, equipment used in the process and Technology. Perform your workplace hazard assessment including identification of potential resonances of accidental release that had a potential for catastrophic consequences in the workplace. Consult with employers and their representatives on the development and conduct of hazard assessments. And development of chemical accident prevention plans.
How the standard works:
Established systems to respect the workplace hazard assessment findings we shall prevent prevention mitigation and emergency responses. Review periodically the workplace hazard assessment and response system.
Develop and return operating procedures for the chemical process including procedures for each operating page operating limitation safety and health considerations.
Hazard assessment and response system
To understand PSM and its requirements, employers and employees need to understand how OSHA uses the term process means in any actually involving a highly hazardous chemical
Process safety information:
Employees must complete compilation of Return process safety information before conducting any process hazard analysis required by the standard.
The compilation of the return process as hazard analysis by the standard.
Information on the hazards of the highly hazardous chemical:
- toxicity
- permissible data
- reacting data
- Corrosive data
- thermal and chemical stability data and hazard on the effects.
Information on the technology of the process:
- Block diagram
- process chemistry
- minimum invented inventory
- scope of upper and lower limits for such items temperatures ,pressures,flows of compositions.
- An evaluation of the consequences of deviation including those affecting the safety and health of employees.
- Information on the equipment
- Materials of construction
- Piping and instrumentation diagram
- Electrical classification
- Ventilated system and design
- Relief system and design basis
- Design codes and Standards employed.
- Materials energy and balances of process.
The compilation of the above-described causes used in safety information provide the basis for identifying and understanding the hazards of a process and it is necessary in developing the hazards of a process in a hazard analysis.
Process hazard analysis:
Hazard analysis orderly systematic approach for identifying involving highly hazardous chemicals. Employers must form an initial process hazard analysis(hazard evaluation) on all processes covered by the standard. The process analysis methodology selected must be only possible to the complexity of the process and must identify and evaluate and control the hazards involved in the process.
The employer must use the following methods to approve the appropriate to determine and evaluate the hazards of the process.
- what if
- checklist
- hazard and operability studies (Hazop)
- failure mode effect analysis
- fault tree analysis
Hazop study:
Traditionally Hazop and PHA are two sessions held separately producing data bases. In the integrated method and risk matrices, Hazop brings structure, procedure,and its criteria.(mainly use of nodes, keywords and deviation). While the risk matrix case brings to this hybrid technique the capacity to prioritize risks/ deviations in order to provide a more detailed implementation plan.
Objectives of Hazop study:
Hazop in the process industry may be focused either to the assessment of safety with a consideration of a possible risk for both the equipment and the operators) or the operating(with regard to keeping required quantity of the product).
- possibility of Degradation/ decomposition of raw materials.
- possibility of human factors.
- possibility of an exothermic reaction decomposition of hazard from the material, reaction mixture and final product.
- possibility of an undesired reach.
- possibly utility failure.
Traditionally hazop study technique is guarded by word application(such as more or less) a process variable(temperature ,flow, pressure). In this Quantitative approach for a risk matrix. Course of the method is the use of Hazop and diagnosis method) parameter, guide word and deviation for each node) from that the causes of consequences related to deviation or investigated. From the Hazop spreadsheet
Guide word-deviation-cause-consequence.
using the synonym.
| NOMLAPRO | |
| guide word | Meaning |
| No or not | Complete negative of design intent |
| More | Quantitative increase. |
| Less | Quantitative decrease |
| As well as | Quantitative Modification/ increase opposite |
| Reverse | Logical design |
| Other than | Complete substance |
| Early | Relative to clock time |
| Late | Relative to clock time |
| Before | Relating to order |
based on temperature, flow, pressure ,and level.
During Commissioning and decommissioning Hazopis very useful.
Failure mode effect analysis:
Systematic structure technique for failure analysis. It was developed by reliability engineers in the late 1950 to study the problem that might arise from Malfunctioning of military systems. FMEA is often the step of your reliability study. It involved reviewing as many as many components, assemblies, and subsystems as possible to identify failure modes and their causes and effects. There are numerous variations of such worksheets.
An FMEA can be a qualitative analysis, but may be put on your quantitative analysis when mathematical failure occurs.
A few different types of FMEA analysis exist
- *Functional
- *Design
- *Process
FMEA can be extended to FMECA(failure mode, effects, criticality analysis)
FMEA a is the inductive reasoning(forward logic) single point failure analysis and Is a care task in reliability engineering, safety Engineering and quality engineering.
A Successful FMEA activity helps to identify potential failure modes based on common physics of failure logic. It is widely used in development and manufacturing industries in various stages of the product life. Effect analysis refers to the studying of consequences of those failures on different system levels.
Functional analysis needed as an input to determine correct failure modes or piece- part(hardware) FMEA. An FMEA used structural mitigation for Risk reduction based either on failure or both. The FMEA is in principle a fall inductive(forward) logic analysis.
Fault tree analysis
FTA is a top down deductive failure analysis in which an undesired system state office system is analysed using Boolean Algebra. This analysis is mainly used in the fields of Safety Engineering and reliability engineering. To understand how the systems can fail to identify the best to reduce risk or to determine to reduce risk or to determine even rates of your safety accident or a particular system functional failure.FTA is used in aerospace engineering nuclear power chemical process for pharmaceutical petrochemical other industry but is also used as diverse as risk factor> identification relating to social service system failure> it i. It is also used in software engineering for debugging purposes and is closely related to cause. elimination technique used to detect bugs.
Standard operating procedures:
The employer must develop and implement written procedures with process safety information that provide clear instructions for the safety conductor activities involved in each covered process.OSHA believes the tasks under procedures related to the covered process are appropriate consistently and most importantly.
Steps for each operating phase;
- Initial startup
- Temporary operations
- Emergency shutdown.
Including the conditions under which shutdown is required and the assignment of shutdown responsibility to qualified operators to emergency shutdown in safe and timely manner.
- normal shutdown
- startup following turn around for emergency shutdown.
Operating limits:
- Consequences of deviation
- Steps to correct or avoid deviation
Safety and health considerations;
- properties of hazards presented by the chemicals used in the process.
- precautions necessary present to exposure including engineering controls and personal equipment .
- control measures to be taken if physical contact or Airborne exposures.
- quality control for raw materials and control of various hazardous chemical inventory levels.
- any special or unique hazards
- safety system.
Employee participation:
Employers wrote a plan of action to implement employees for participation required by PSM.
Under PSM mass conduct with employers and the representation on the contact and development of processes order analysis and other development of the new elements of process management, they provide two employees and their representation access to process hazard analysis and also to other information required to be developed by the standards.
Training:
OSHA believes that the implementation of an effective training program is one of the important steps one can take to hang nonce presently involved in the operating process in an interview of the process and in its procedures. Did training's goals emphasizing on the specific safety and help hazards of the process. Emergency including shutdown and other safe work practices that applied to the Employees job tasks. These employees are already involved in operating a process as PSM. Effective dates do not necessarily need to be given for initial training instead the employer must certify in meeting that their employees have the required knowledge of skills to carry out the direction and responsibilities in operating procedure.
Refresher training:
Refresher training must be provided at least every three years more if necessary to each employee involved in operating a process to ensure that the employee involved in operating a process that he understands and adverse correct operating procedure of the process. The employer in consultation with employees involved in operating the process must determine the appropriate frequency of refresher training.
Trainee documentation
The employer must determine whether each employee operating a process
Received and understood by the process safety management. A record mast big cat carrying The Identity of the employee, the date of training, how the employer verifies that the employee understood the training.
Contractors:
Many categories of contract labor will be present at a job site, search workers may operate the facility or do only a particular aspect of a job because they have specialized when there is a need for increased staff quickly such as a turnaround operation including PSM .
PSM therefore applies to contractors performing maintenance or repair turnaround. Major renovation specified work or adjacent covered process does not apply, however for contractors providing incidental services that do not influence process safety., food clothing, laundry, janitorial, cleaning or other supply services.
Employees representation: When selecting a contractor, the employer must implying obtain and evaluate information regarding contract employee safety performance and programs. The employer also must inform the contract employer of the known potential, fire and explosion and toxic material release hazards related to to workers work related to the contract is work and the process explain to contract employees the applicable provisions of the emergency Action Plan. It should be explained to the contract employees applicable provisions of the Emergency Action Plan develop and implement safe work practices to control the resonance entrance and exit of contract employees in covered process areas, evaluate the presence of contract employees in fulfilling their obligations and maintain the contractor employee injury and illness to be logged.
Pre- startup safety review:
It is Important that a safety review takes place and chemicals are introduced in the process. PSM therefore requires the employee to perform pre- safety review for new facilities and for modified facilities when the modification is significant enough to require a change in the process safety information
- construction and equipment are in accordance with design specification.
- safety, operating, maintenance emergency procedures or in place and are adequate
- process hazard analysis has been performed for new facilities before starter and modified new facilities meet the management of change requirements.
- training of each employee involved in operating a process has been completed.
Mechanical integrity:
OSHA says it is important to maintain critical process equipment design and install correctly and operate properly. PSM mechanical integrity replying to the following equipment.
- pressure vessels and storage tanks
- piping systems(including wiping components such as valves)
- relief fund wind systems and devices
- emergency shutdown systems controls(including monitoring devices, sensors, alarms and interlocks)
- pumps
The employer must establish and implement written procedures to maintain ongoing integrity of the process equipment in an overview of the process and its hazards and trends in the procedures. Description of the inspection for test performed and results of the inspection and in constructing plant equipment ,the plan of the employer must ensure that the fabrication is suitable for the process application. and appropriate checks and inspections shall be done.
Hot work permit:
Permits must be issued for hot work operations conducted near a covered process. The permit must be dominated that fire protection represented in OSHA regulations have been implemented. Prior to the beginning of hot work operations it must indicate the date authorized for hot work and identify the object on which hot work and identify the object which art work is to be performed. Permit must be kept on file until the completion of the heart work.
Management of change:
OSHA believes that contemplated to a process must be evaluated to fully e s s that impact on employee safety and health to determine needed changes to operating procedures. To this end the standard contains a section on procedure for managing processes. Written procedures to manage the process chemicals, technology, equipment and procedures to facilitate that effective covered process must be established and implemented.
- following considerations or or addressed prior to prior to any change.
- impact of the change on employee safety and health
- modifications to operating procedures
- necessary time period for the change
- authorization requirement for the proposed change.
Employees who operate your process and maintenance and contract employees whose job takes will be affected by a change in the process must be informed of and if you change covered by the process and the procedures in a change covered by the process safety information. Such information should be updated about the process. If a change covered by this procedure change is required for operating procedures for practices they have to be adopted.
Incident investigation:
Crucial part of the process safety management program is a thorough investigation of incidents to identify the chain of events and causes so that correction measures can be developed and implemented. AccordinglyPSM psm requires an occasion of each that resulted in or could reasonably have resulted in a catastrophic release of a highly hazardous chemical in the workplace.
Such an incident investigation must be investigated properly but not later than 48 hours following this season. The investigation team consists of at least one person knowledgeable in the process involved including a contract employee if the incident involves.
An investigation report must be prepared within 48 hours
- date of incident
- date of Investigation began
- description of the incident
- factors that contributed to the incident
- recommendation from the investigation team.
A system must be established to promptly address and resolve report findings and recommendations, resolutions and corrective actions must be documented and the reward by all affected personal job tasks are relevant to the incident facilities report for five years .
Emergency and planning:
In spite of PSM being on force, if an incident occurs it is essential that emergency pre-planning make employees aware and able to execute proper action. For this reason an emergency action plan for the entire plant must be developed and implemented in accordance with the provision of other rules(29)FR. In addition emergency plan action must include handling and releases of hazardous chemicals. Employees under PSM also are subject to the OSHA standard of hazardous waste and emergency response regulations.
Compliance audit:
To be certain process safety information is effective, employees must certify that I have evaluated compliance with provisions of PSM at least every three years. This will verify with the procedures and practices developed under the standard by at least knowledgeable in the process and a report of the findings of the audit must be developed and documented the deficiencies that have been corrected.
The two most recent complaint audit reports must be kept on file.

By V. Narasimhan, Global Safety Consultant Chennai



